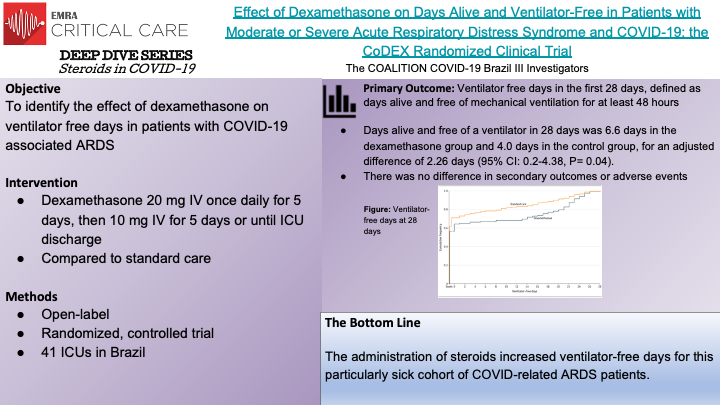
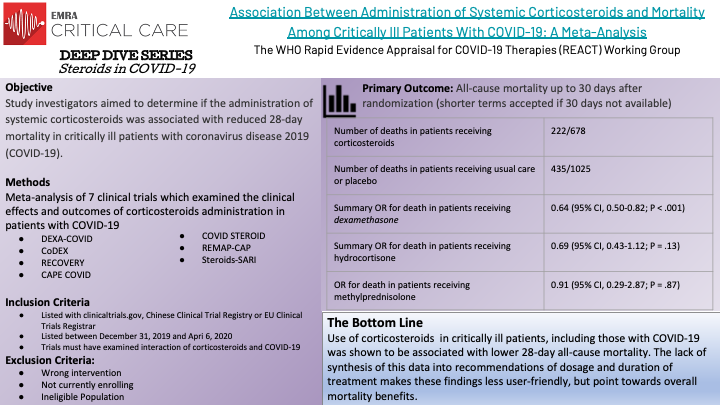
This EMRA Deep Dive will examine the trials that currently guide corticosteroid use in COVID-19 related respiratory failure.
BACKGROUND
The role of corticosteroids in severe infections, sepsis and ARDS has been a constantly evolving discussion and remains controversial. The recent APROCCHSs, ADRENAL and DEXA-ARDS along with other prior data have shown the benefits of corticosteroids for sepsis and ARDS, however their use is not universal.1,2,3 The COVID-19 pandemic has further highlighted the need for strong RCTs to guide appropriate management.
CONCLUSION
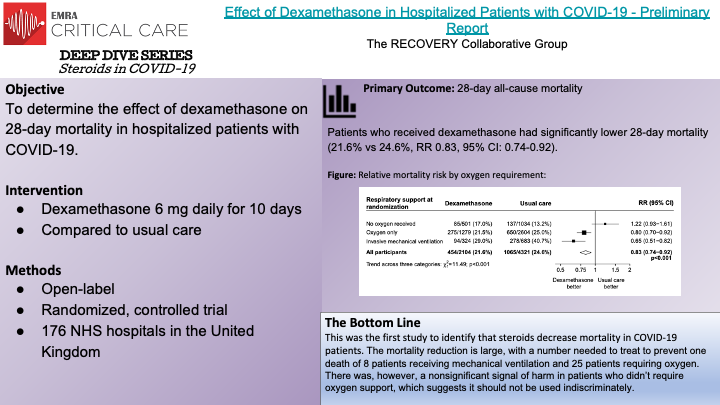
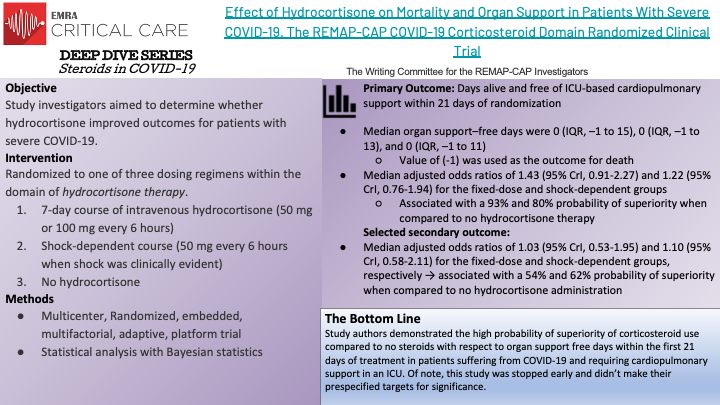
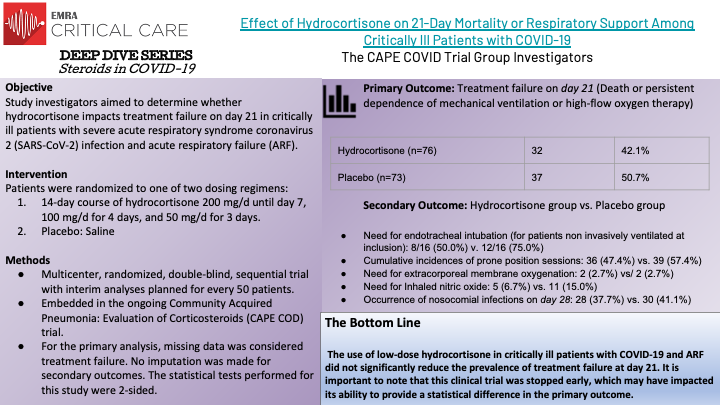
Corticosteroids have demonstrated safety in the critically ill and have proven benefits for patients in sepsis and septic shock. This appears to remain true for COVID-19 infections requiring oxygen. Following the results of these aggregate studies, the WHO recommends systemic corticosteroids for patients with COVID-19 infection requiring oxygen.
Access the PowerPoint deck or read on to view the slides.
Read the full Critical Care Alert.
Read the full Critical Care Alert.
Read the full Critical Care Alert.
Read the full Critical Care Alert.
Read the full Critical Care Alert.
REFERENCES
- Annane D, Renault A, Brun-Buisson C, et al. Hydrocortisone plus Fludrocortisone for Adults with Septic Shock. N Engl J Med. 2018;378(9):809-18.
- Venkatesh B, Finfer S, Cohen J, et al. Adjunctive glucocorticoid therapy in patients with septic shock. N Engl J Med. 2018;378(9):797-808.
- Villar J, Ferrando C, Martínez D, et al. Dexamethasone treatment for the acute respiratory distress syndrome: a multicentre, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Resp Med. 2020;8(3):267-76.